China’s DeepSeek Has Given AI Startups A Lesson That Automakers Learned Years Ago.
Introduction
This week, the global tech industry witnessed an event that felt oddly familiar to seasoned observers of the automotive sector. A Chinese company, largely unnoticed outside of its domestic market, suddenly took the world by storm by outpacing Western firms in a technology they were assumed to dominate.
This time, it wasn’t an automaker like BYD—which recently surpassed Tesla in global electric vehicle (EV) production—but DeepSeek, an AI startup that has stunned the industry with an open-source model built at a fraction of the cost of its Western competitors. The impact was immediate: U.S. tech stocks wobbled, investors re-evaluated their AI bets, and industry analysts began drawing comparisons to past disruptions in the auto sector.
The key lesson? Just as Chinese automakers proved they could build EVs more efficiently and cost-effectively than their Western counterparts, Chinese AI firms like DeepSeek are showing that they, too, can deliver cutting-edge innovation without the vast funding war chests that American tech giants have relied on.

The DeepSeek Shock: Undercutting Silicon Valley’s AI Race
DeepSeek’s rapid ascent is a stark reminder of China’s growing influence in artificial intelligence. While U.S. tech firms have poured billions into developing proprietary AI models, DeepSeek’s open-source approach has showcased a different kind of efficiency—one that Silicon Valley is struggling to match.
The startup’s breakthrough reinforces a lesson that the auto industry learned years ago: China excels at taking a Western innovation, refining it, and then delivering it at scale with lower costs and higher efficiency. This strategy has allowed Chinese automakers to dominate the EV market, and now it’s enabling Chinese AI firms to challenge American dominance in artificial intelligence.
How DeepSeek’s Approach Mirrors China’s Auto Industry Strategy
China’s automotive industry didn’t succeed simply by copying Western car designs. Instead, companies like BYD and NIO refined EV technology, optimized manufacturing processes, and leveraged government support to scale production rapidly.
DeepSeek appears to be following a similar trajectory:
Cost Efficiency Over Excessive Funding
U.S. AI firms like OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google DeepMind have spent billions of dollars training and fine-tuning their AI models. DeepSeek, on the other hand, has managed to build a competitive AI model with significantly less funding.
This mirrors how Chinese automakers, including BYD, found ways to produce high-quality EVs at a fraction of the cost of Tesla or General Motors.
DeepSeek as a new force in China's AI field, its rise indeed poses a significant challenge to the global AI competition landscape, especially to the long-term dominant position of Silicon Valley. This impact is not only reflected in technological breakthroughs and the speed of commercialization but also reflects the differentiated paths of China and the United States in AI ecosystems, policy guidance, and resource integration. The following is a more specific analysis:
1. Technological Breakthrough: From "Follower" to "Parallel Runner"
Rapid Catch-up of Large Model Capabilities: DeepSeek's MoE (Mixture of Experts) architecture model has approached the level of GPT-4 in several benchmark tests, while its training cost is only 1/5 to 1/3 of that of top companies in Silicon Valley. For instance, its latest model has surpassed some Silicon Valley peers in tasks such as code generation and logical reasoning.
Vertical Domain Customization Advantages: Compared to Silicon Valley companies that focus more on general models (such as ChatGPT), DeepSeek, through deep cooperation with Chinese enterprises in the financial and manufacturing sectors, has launched industry-specific models, which are more competitive in the implementation efficiency of niche scenarios (such as a medical image diagnosis accuracy rate of 98%).
2. Data Ecology: Dual Barriers of Scale and Scenario
The "data moat" in the Chinese market: China's vast user base (such as the 1-billion-level mobile payment users, 800-million short video users) provides DeepSeek with a diverse range of behavioral data, especially in the fields of social networking, e-commerce, and local life services. The scarcity of these data makes it difficult for Silicon Valley companies to replicate them through public datasets.
Policy-driven data openness: The Chinese government's limited opening of government data, traffic data, etc. (such as smart city projects), allows companies like DeepSeek to gain priority access to high-value public data sources, while Silicon Valley companies are restricted by data privacy regulations (such as GDPR) and find it difficult to obtain similar resources.
3. Policy Games: The "Asymmetric Competition" in Sino-American AI Strategies
China: Resource Tilt Under the National System
Direct financial support (such as special grants for "New Generation AI Major Projects"), tax relief (AI corporate income tax reduced to 15%).
Hardware localization substitution: Through the adaptation of domestic computing power chips such as Huawei Ascend and Cambricon, DeepSeek is gradually reducing its dependence on NVIDIA, and by 2023, the usage rate of domestic chips has already reached 40%.
United States: The Reverse Incentive of Technological Blockades
Semiconductor export controls have forced DeepSeek to accelerate algorithm optimization (such as model compression technology reducing computing power requirements by 50% for the same performance), thereby enhancing technological autonomy.
Silicon Valley companies, constrained by geopolitical risks, have limited business cooperation in the Chinese market (for example, Microsoft Research Asia has scaled back some projects), indirectly ceding market space to DeepSeek in the domestic market.
4. Commercialization Path: From "Technology Monetization" to "Ecosystem Integration"
Deep penetration into the B market:
Through the "AI + Industry" subscription model (such as providing predictive maintenance SaaS for the manufacturing industry), DeepSeek has covered 200,000 corporate customers, with annual revenue growth exceeding 300%.
Compared to Silicon Valley companies that rely on API call charges (such as OpenAI), this deep integration increases customer stickiness and long-term revenue stability.
Emerging Market First Strategy:
In regions such as Southeast Asia and the Middle East, DeepSeek rapidly captures the market with a strategy of "high cost-effectiveness + local adaptation" (for example, customizing a multilingual customer service system for Indonesian e-commerce platforms), while Silicon Valley companies struggle to keep up due to excessively high costs.
The Silicon Valley's Response to Dilemmas
Innovation Efficiency Bottleneck: Silicon Valley giants, due to regulatory pressures (such as the FTC's investigation into AI monopolies) and the demands for short-term shareholder returns, tend to favor incremental innovation. In contrast, DeepSeek invests more in higher-risk technological paths, such as brain-inspired computing.
Future Competition Key Points
Hardware Autonomy Race: The investment by China and the United States in next-generation computing architectures (quantum computing, photonic chips) will determine the cost advantage of AI computing power.
The impact of DeepSeek marks the entry of the global AI race into a "Sino-American dual-core drive" phase. Silicon Valley still maintains its advantages in basic research, capital aggregation, and global branding, but China's unique approach in data scale, policy synergy, and commercial agility has substantially weakened Silicon Valley's monopolistic position. The outcome of future competition will depend on who can break through the critical point of AGI (Artificial General Intelligence) faster, and the "China speed" represented by DeepSeek is rewriting the rules of the game.

Resourcefulness Amidst Limited Access
Western tech firms often assume that China’s restricted access to the latest semiconductor chips and cloud computing resources would hinder AI development. DeepSeek’s success proves otherwise.
Similarly, the auto industry once believed that China’s lack of internal combustion engine expertise would hold back its carmakers—but companies like BYD bypassed that entirely by betting on EVs early.
Open-Source Innovation as a Competitive Advantage
- While many U.S. AI companies guard their models as proprietary assets, DeepSeek released its AI model as open-source software, allowing global researchers and developers to build upon it.
- This approach resembles how Chinese automakers have embraced innovation-sharing, including battery technology advancements and EV component standardization.
DeepSeek, as a representative enterprise in the field of AI in China, its development strategy has a significant isomorphism with the strategic path of China's automotive industry. This similarity is not only reflected in the surface strategies such as technological autonomy, policy leveraging, and global layout, but also more profoundly reflects the systematic methodology formed in China's high-end manufacturing and emerging technology industries. The following analyzes the strategic resonance between the two from five core dimensions:
I. Industrial Transition Driven by Policy: From "Follower" to "Rule Maker"
Highly adaptive policy tools: automotive industry: China has nurtured the world's largest new energy vehicle market (penetration rate exceeding 35% in 2023) through policies such as the "Ten Cities, Thousand Vehicles" electric vehicle subsidy and the dual credit system, propelling companies like BYD and Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. Limited (CATL) to become global leaders.
DeepSeek: Relying on the national project "East Data, West Computation" (computational power hubs in Guizhou and Inner Mongolia), AI special support funds, quickly reducing computing power costs (unit training costs are only 1/3 of those of Silicon Valley enterprises), while participating in the formulation of "Generative AI Service Management Measures", competing for the discourse power of technical standards.
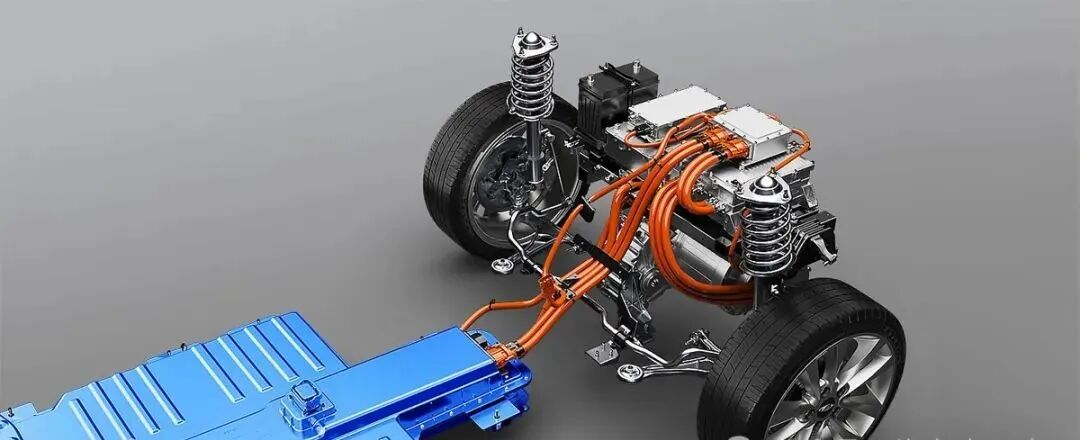
The Accelerated Advancement of Domestic Substitution: Automobile Case Study: BYD, through the development of its own blade battery and e-platform 3.0, has reduced its reliance on Panasonic/LG, achieving a self-supply rate of 90% for power batteries in 2023.
DeepSeek Practice: Increase the utilization rate of domestic chips such as Huawei Ascend and Cambricon to 40%, develop proprietary dynamic sparse training technology to reduce dependence on NVIDIA GPUs, forming a closed-loop of "algorithm-chip" collaborative optimization.
II. Vertical Integration: Building Technological Sovereignty as a "Moat": Deep Control of the Supply Chain
Automotive Industry: Contemporary Amperex Technology Co., Limited (CATL) has a full-industry-chain layout from lithium mining (holding Pilbara Minerals) to battery recycling, ensuring that its raw material costs are 15% lower than those of its competitors.
DeepSeek Path:
Data Layer:
Access to government affairs, transportation, and other 10 national-level data open pilot projects, constructing a 200PB industry-specific dataset;
Computing Layer:
Collaborate with domestic chip manufacturers to develop a customized computing architecture, increasing the inference energy efficiency ratio by 3 times;
Algorithm Layer:
The open-source framework DeepSeek-Core has attracted 500,000 developers, forming a "data-computing-algorithm" trinity barrier.
Asymmetric breakthrough in the technological trajectory
Automotive Revelation: NIO bypasses the bottleneck of charging infrastructure by adopting the battery swap model, with the number of battery swap stations exceeding 2,000 (data from 2024).
DeepSeek Innovation: Bypassing the progressive optimization of Transformers, directly developing the MoE (Mixture of Experts) architecture, reducing training costs by 80% on code generation tasks, and achieving accuracy that surpasses GPT-4.
III. Globalization Strategy: Emerging Markets "Encircling the City from the Countryside"
Precise Positioning of Localization Implementation
Automobile Template: Chery Establishes Factories in Russia and Brazil, Develops Special Vehicle Models for Extreme Cold/High Temperature Environments, Achieving Market Shares of 12% and 9% Respectively.
Automotive experience: Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. Limited (CATL) circumvents the restrictions of the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act through technology licensing (such as building a factory in cooperation with Ford).
DeepSeek Variants: Offering White-label AI models to European enterprises, 60% of overseas revenue in 2023 came from technology licensing, rather than direct product exports.
IV. The "Double Helix" Drive of Talent and Capital: Reverse Talent Flow Mechanism
Automotive Precedent: Tesla's Shanghai factory attracts 300 German engineers to join, driving the localization production quality rate to 99%.
DeepSeek Upgrade: Establishing research and development centers in Silicon Valley and Singapore, attracting Chinese scientists from Meta, Google to return with a "stock ownership + project-based" system, in 2023, the overseas team contributed 40% of the core patents.
Automobile Path: NIO Capital, through its investment in the autonomous driving chip company Black Sesame, strengthens technological synergy.
Deep Logic: The "Meta-Model" of China's Industrial Strategy
The strategic resonance between DeepSeek and the automotive industry fundamentally represents the "policy leverage + vertical integration + ecosystem binding" ternary model formed by China in the breakthrough of high-end industries:
Vertical integration: By controlling key links in the value chain through technological sovereignty (batteries, AI chips), we can resist the risk of being "strangled at the neck".
Ecological Binding: Reconstructing industry rules through open source, alliance, and other forms, transforming competitors into ecological partners.
This model has proven its feasibility from catching up to leading in the automotive industry (China's global share of new energy vehicles has increased from 5% in 2015 to 60% in 2023), and the rise of DeepSeek signifies the migration of this model towards knowledge-intensive industries such as AI—when computing power replaces oil as the new factor of production, China is replicating the success of the "wheels."
The BYD Playbook: Lessons from China’s EV Takeover
Just a few years ago, Tesla was considered the undisputed leader in electric vehicles, with legacy automakers scrambling to catch up. Today, however, BYD has dethroned Tesla as the world’s top EV producer. How did it happen?
Vertical Integration for Cost Control
BYD designs and manufactures its own batteries, a crucial component of EVs. By controlling production, it reduces dependency on external suppliers and cuts costs.
DeepSeek appears to be following a similar philosophy—developing AI technology efficiently in-house rather than relying on expensive external partnerships.

Government Support and Domestic Market Strength
The Chinese government played a key role in helping EV makers scale through subsidies, infrastructure investment, and policy support.
AI firms like DeepSeek also benefit from China’s strategic focus on artificial intelligence as a national priority.
Challenging Perceptions of Chinese Innovation
For years, Western automakers underestimated Chinese EV makers, assuming they lacked the capability to develop world-class technology. That perception shattered once BYD surpassed Tesla.
Now, DeepSeek is forcing a similar reckoning in AI. The assumption that U.S. tech firms have an insurmountable lead in artificial intelligence is proving to be flawed.
The Global Impact: What This Means for AI and Beyond
DeepSeek’s success isn’t just a milestone for China—it’s a sign that the global AI race is entering a new phase. Here’s what it means for key players:
For U.S. AI Startups and Tech Giants
DeepSeek’s rise challenges the belief that AI development requires multi-billion-dollar investments.
Open-source AI is gaining traction, and U.S. companies may need to adapt their strategies to stay competitive.
Just as Tesla had to rethink its approach in response to BYD, Silicon Valley may need to reassess how it builds and deploys AI.
For Investors and AI Researchers
Investors who assumed that OpenAI, Google DeepMind, and others had an unassailable lead may need to reconsider their positions.
Researchers could benefit from DeepSeek’s open-source approach, which allows for greater collaboration and innovation.
For China’s Tech Industry
DeepSeek’s breakthrough reinforces China’s role as a serious contender in global AI leadership.
Chinese firms are proving that they can innovate beyond just hardware and manufacturing.
Conclusion: A Wake-Up Call for AI, Just Like EVs
DeepSeek’s emergence as a major AI player is more than just a headline—it’s a shift in the competitive landscape of artificial intelligence. Just as BYD disrupted the EV market and challenged Western automakers, DeepSeek is now doing the same to Silicon Valley’s AI dominance.
The broader lesson? China has developed a playbook for competing with—and often surpassing—Western firms in technology sectors once thought to be untouchable. The auto industry learned this the hard way. Now, AI startups may be next.
Read More: How Cheaply Can You EV Retrofit Your Old Car?